11.1 What Is A Volcano? Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition
A mountain is a natural rise in the Earth's surface which is usually formed as a result of crustal movements on the planet. On the basis of how they are formed, mountains are categorized into five different types - fold mountains, fault-block mountains, plateau mountains, dome mountains and volcanic mountains.
New Zealand sits across two continental plates, and White Island is just one of its many
Vocabulary A volcano is an opening in a planet or moon's crust through which molten rock, hot gases, and other materials erupt. Volcanoes often form a hill or mountain as layers of rock and ash build up from repeated eruptions. Volcanoes are classified as active, dormant, or extinct.
Volcano anatomy diagram. Vector Illustration. 594028 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Feel the ground. It's nice and cool, right? Well, dig down a few kilometers and things really heat up. Once you're down more than 30 km, and temperatures can reach more than 1,000 degrees C; that's.

Volcano Eruption Infographic Vector Download
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): General diagram of volcanic hazards. While the most obvious volcanic hazard is lava, the dangers posed by volcanoes go far beyond lava flows. For example, on May 18, 1980, Mount Saint Helens (Washington, United States) erupted with an explosion and landslide that removed the upper 400 m (1,300 ft) of the mountain.

Why Have Volcanoes in the Cascades Been So Quiet Lately? WIRED
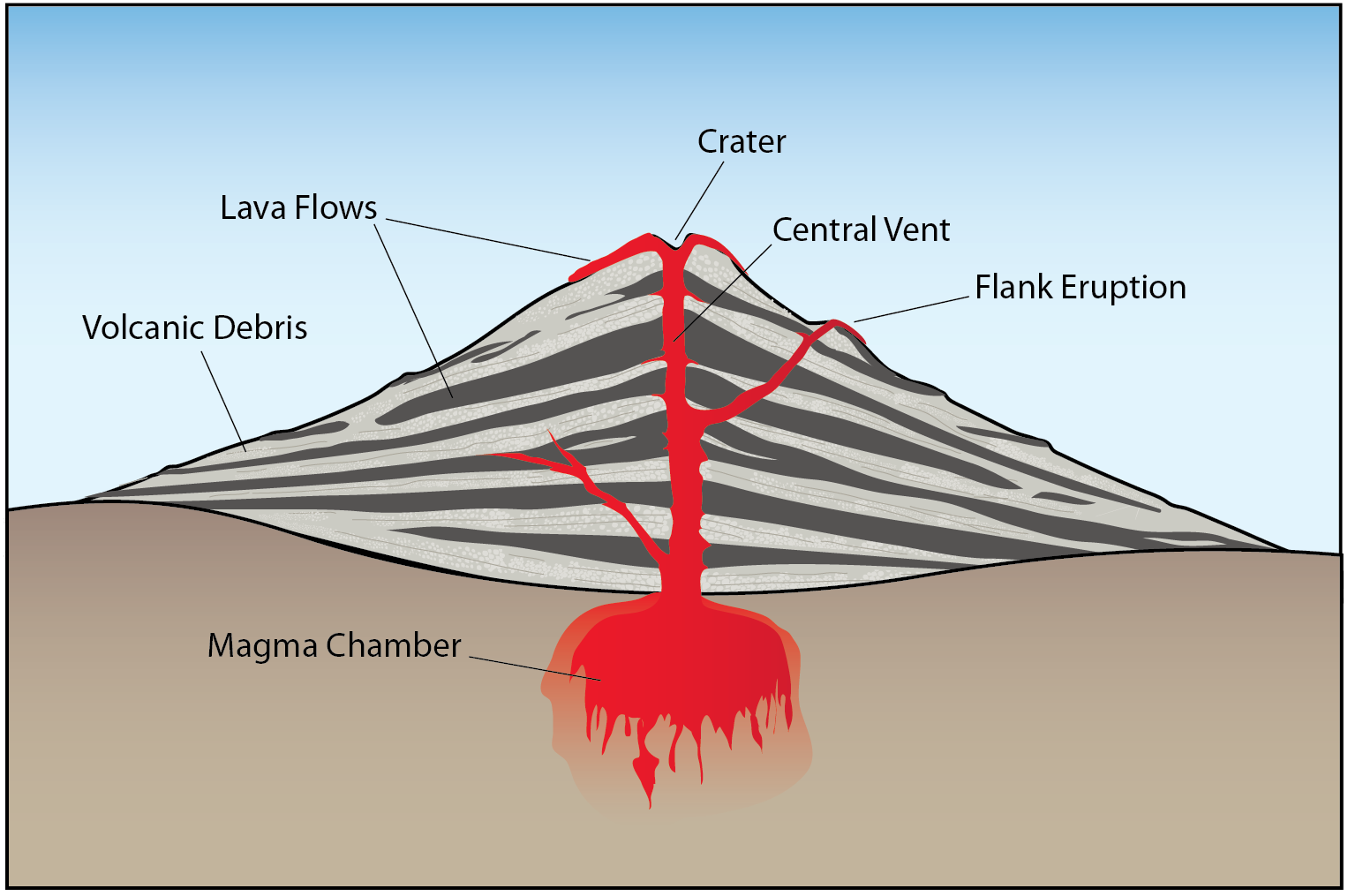
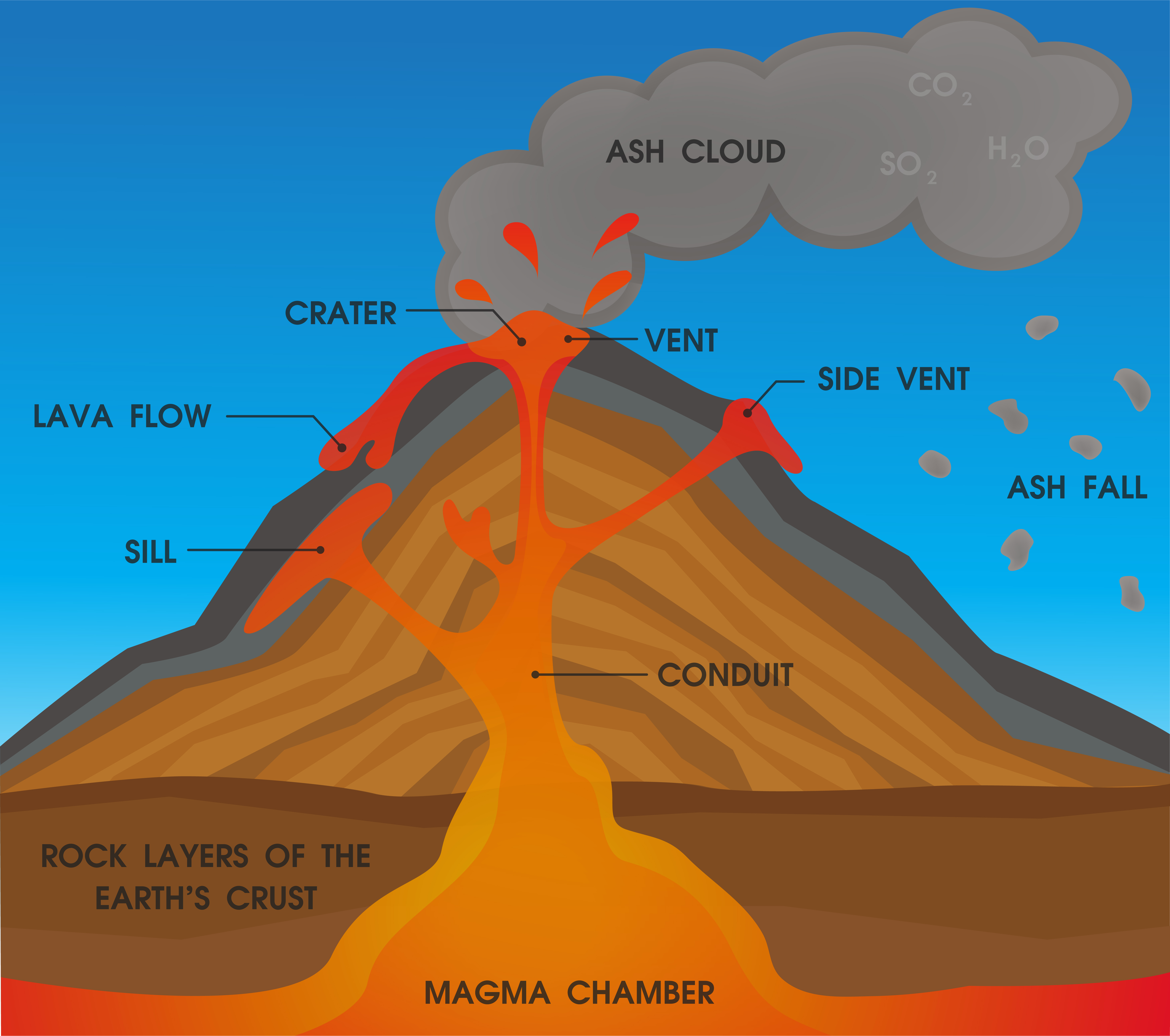
The diagram below shows the main features of a volcano. The magma chamber is a large underground pool of magma. Under pressure, the magma in the chamber can rise up the main vent, which is the central tube through the volcano. Volcanoes typically have a bowl-shaped basin at the top of the volcano, known as a crater.

Volcano infographic isometric style Royalty Free Vector
volcano, vent in the crust of Earth or another planet or satellite, from which issue eruptions of molten rock, hot rock fragments, and hot gases. A volcanic eruption is an awesome display of Earth's power. Yet, while eruptions are spectacular to watch, they can cause disastrous loss of life and property, especially in densely populated.

Volcanic Mountains Diagram
Intro How Volcanic Mountains Are Formed. Fundi Bots 796 subscribers Subscribe 1.2K views 10 months ago One of the most interesting physical features are mountains. In this video, we'll have a.

Pin on GEO
A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where molten rock erupts through the surface of the planet. There are a huge number of active volcanoes present worldwide. In this article, we will learn about the definition, formation and types of volcanoes. Table of Contents What Are Volcanoes? Formation of Volcanoes Different Stages of Volcanoes

Example of a stratovolcano such as Dibankie volcanic mountain... Download Scientific Diagram
A volcano needs a reservoir of molten magma (e.g. a magma chamber), a conduit to allow magma to rise through the crust, and a vent to allow the magma to escape above the surface as lava. The erupted volcanic material (lava and tephra) that is deposited around the vent is known as a volcanic edifice, typically a volcanic cone or mountain.
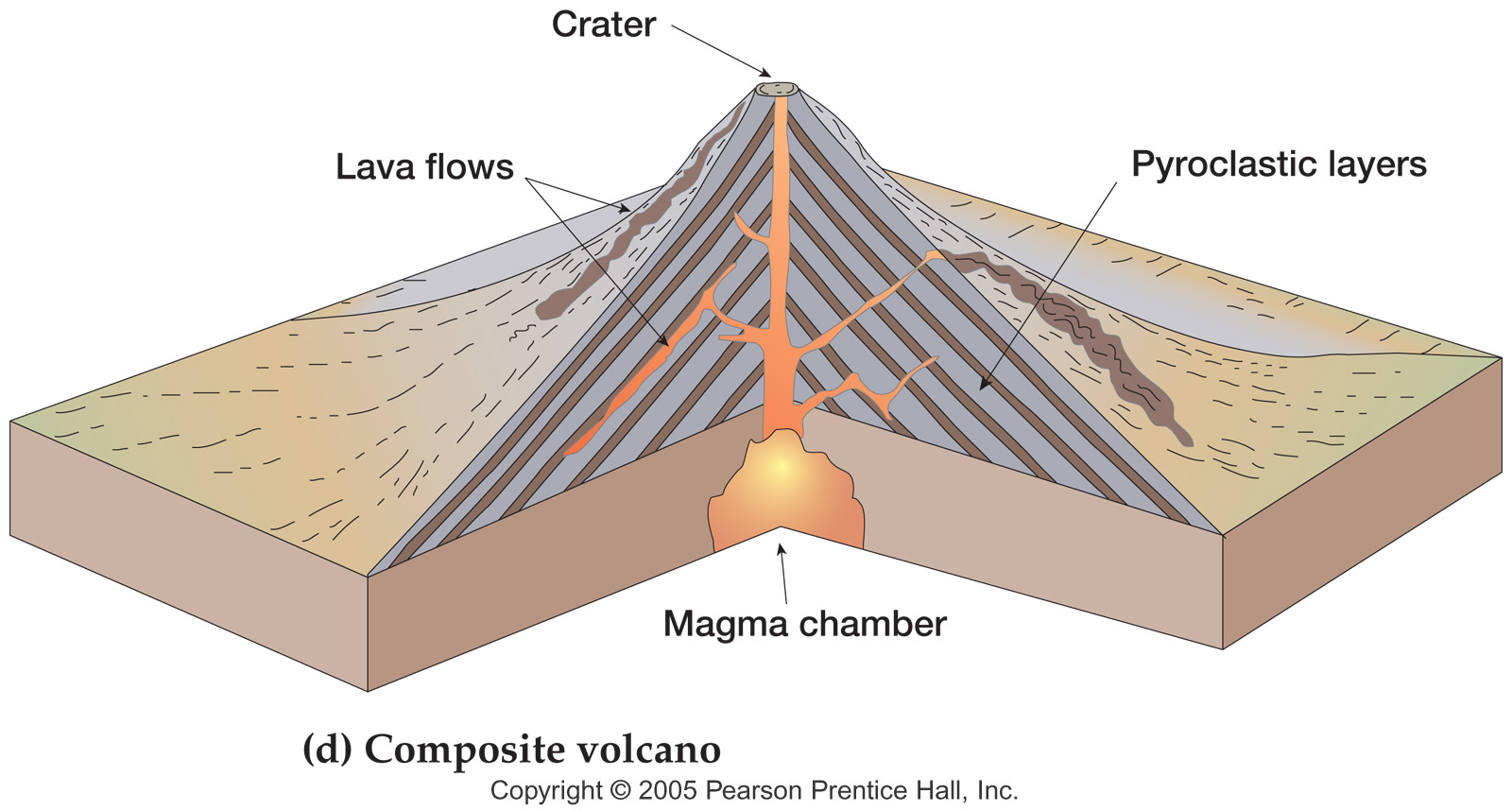
Composite Volcano Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Find out how tectonic movement create volcanic mountains with this BBC Bitesize Scotland article for P5, P6, P7 - Second Level CfE

Potter's Geography Features of a Volcano
A volcano is a feature in Earth's crust where molten rock is squeezed out onto Earth's surface. Along with molten rock, volcanoes also release gases, ash, and solid rock. Grades 9 - 12+ Subjects Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Physical Geography Photograph Shishaldin

VOLCANOS, SUBDUCTION CONVEYORS, & METAMORPHIC ROCKS Vern Bender
In the diagram above, the dike and the volcanic neck—despite the latter's name—are both intrusive features, whereas the fissure, lava flows, and volcanic cone are all extrusive.. The heart of California's Sierra Nevada mountains is carved from a granitic batholith emplaced between about 120 and 85 million years ago. About the Author.
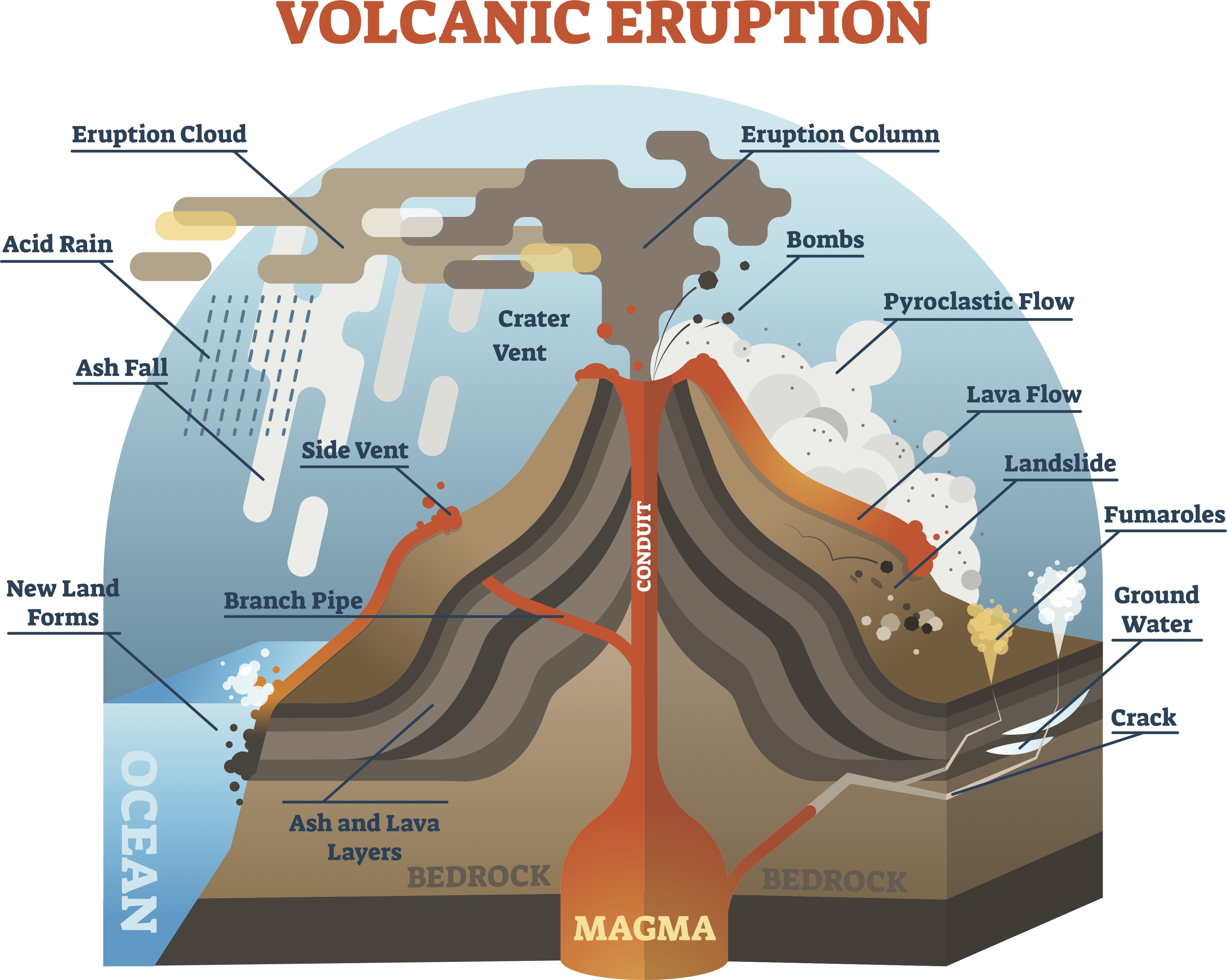
What are lahars and pyroclastic flows? Geography
Central summit, the highest point on the mountain at just over 7,100 ft (2,165 m) rises on the background skyline, 7 km southwest of North Summit. Alaska Volcano Observatory photo USGS scientists monitor over 160 active and potentially active volcanoes in the United States.
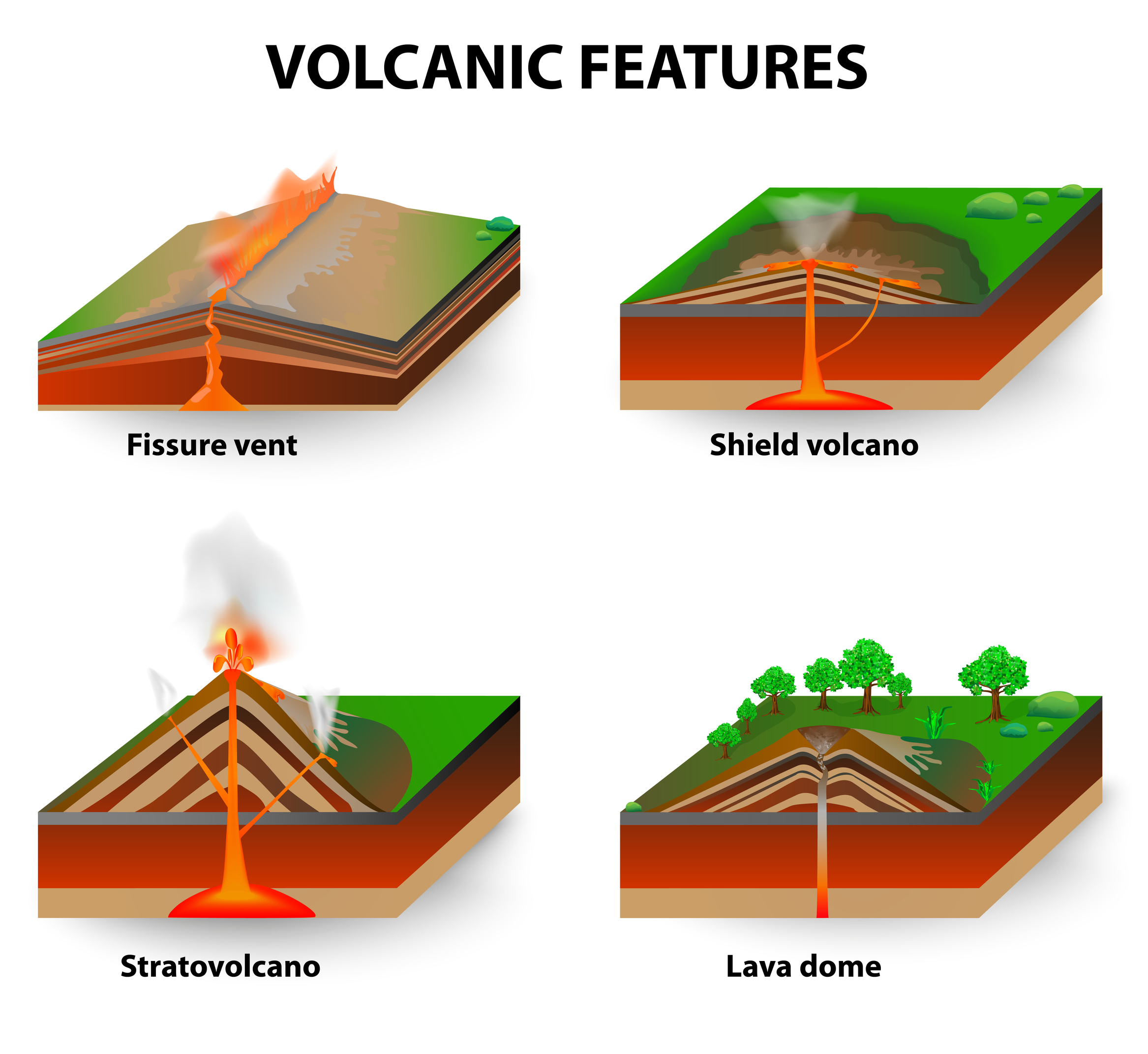
Types of Volcanoes
The mid‐ocean ridge is a continuous, underwater seam of mountains and volcanoes that form where divergent tectonic plates meet. It stretches all around the globe and is more than 64,000 kilometers (40,000 miles) long. The tectonic plates are spreading apart allowing soft molten rock to bubble up between the plates. Once this hardens it forms.

Pin on Classical Conversations
Volcanic mountains are formed from the lava and tephra that come out of a volcanic vent. These mountains are stratovolcanoes whose size increases after each eruption. The lava that comes out of the stratovolcanoes is highly viscous. It does not travel far and starts solidifying near the vent. Slowly a mountain develops around the vent.
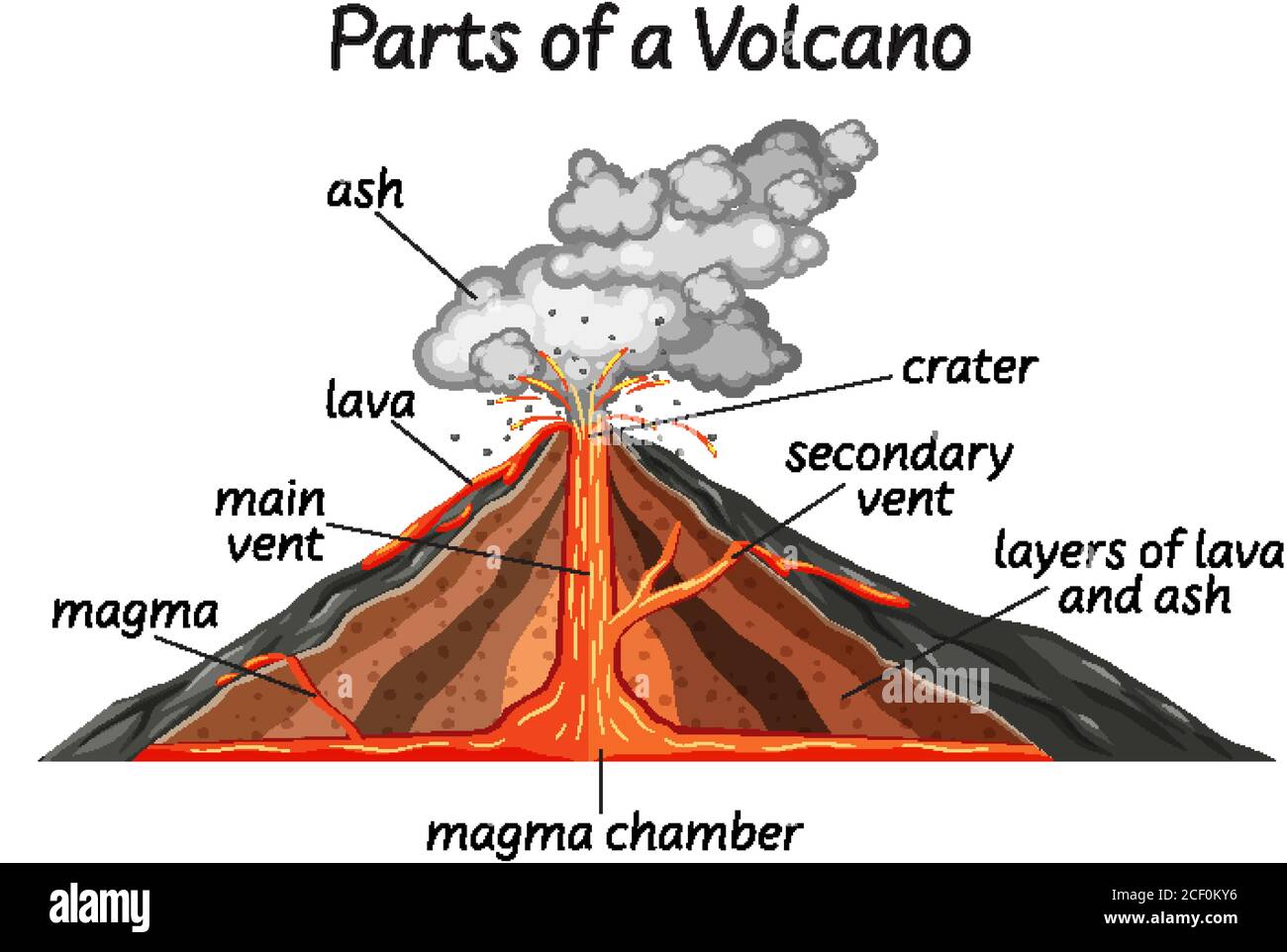
Part of a volcano illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
1. Ash Volcanic ash consists of rock, mineral, and volcanic glass fragments smaller than a tenth of an inch in diameter—or slightly larger than a pinhead. Volcanic ash is quite different from.